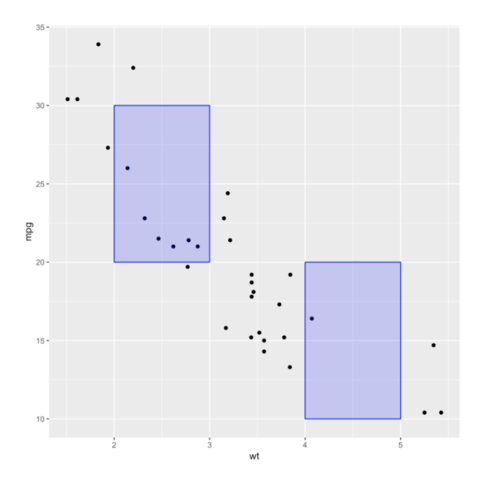
Rectangle
Learn how to use the annotate function to add a rectangle on a specific part of the chart.
Simplify
Simplifying a geospatial object allows to get a lighter object that will be plotted faster.
Rectangle
Learn how to use the annotate function to add a rectangle on a specific part of the chart.

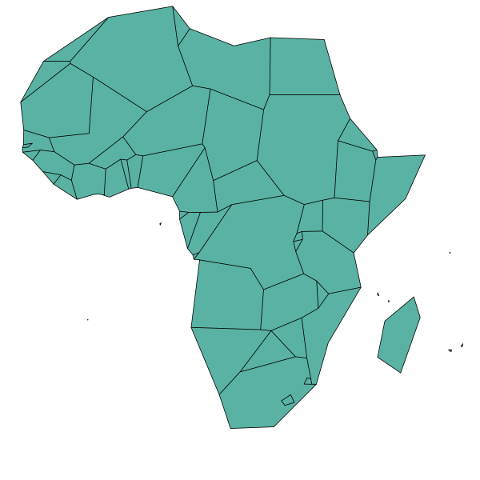
Simplify
Simplifying a geospatial object allows to get a lighter object that will be plotted faster.
